ETCS
ETCS
Je to jednotný celoevropský zabezpečovací systém, který bude zajišťovat jednotnou evropskou železnici a vyšší bezpečnost provozu na ní. Zajistí také, aby vlaky dopravců mohly volně, bez problémů přejíždět z jedné země do druhé.
Je to zařízení, které nahrazuje velké množství různých, vzájemně nespolupracujících a mnohdy zastaralých systémů v jednotlivých zemích.
Zařízení, bez něhož se neobejde budování vysokorychlostních tratí, ale i na klasických tratích zajistí vyšší bezpečnost a zvýšení rychlosti nad 160 km/h.
Potřeba jednotné evropské železnice však není žádnou zcela novou a neznámou problematikou, nýbrž zcela přirozenou součástí vývoje železnice v Evropě, která je nutná pro její konkurenceschopnost a do budoucna i její další existenci. [1]
Funkčnost ETCS
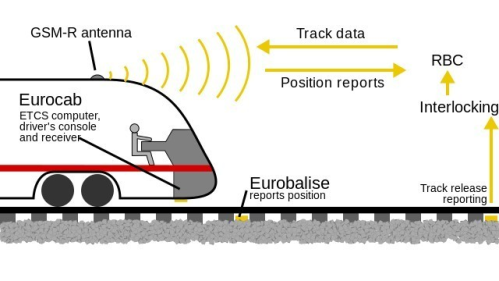
Radiobloková centrála (RBC) a Eurobalízy ve druhé aplikační úrovni tvoří traťovou část ETCS. RBC sleduje jednotlivé vlaky a komunikuje s nimi. Zná pozici, směr jízdy a rychlost vlaků a vyhrazuje pro jejich další jízdu volný, bezpečný prostor. Sleduje, zda strojvedoucí vlaku dodržuje rychlost jízdy a reaguje správně na situaci na trati. Umí zastavit vlak před návěstí Stůj nebo při indispozici strojvedoucího. Aby systém dobře fungoval, musí se postupně vybavit infrastruktura i vozidla všech dopravců, kteří budou chtít na takové trati jet.
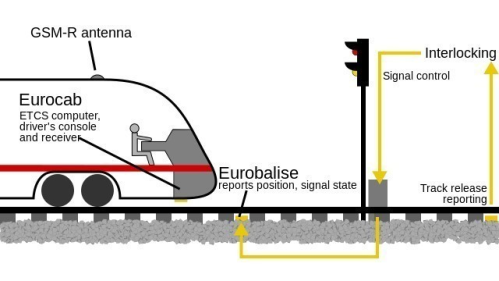
Existuje i jednodušší provedení traťové části ETCS (první aplikační úroveň), které nevyžaduje rádiový systém GSM-R pro komunikaci s vlaky a hodí se zejména na méně zatížené tratě.
ETCS úrovně
Level 0
Level 0 applies when an ETCS-fitted vehicle is used on a non-ETCS route. The trainborne equipment monitors the maximum speed of that type of train. The train driver observes the trackside signals. Since signals can have different meanings on different railways, this level places additional requirements on drivers' training. If the train has left a higher-level ETCS, it might be limited in speed globally by the last balises encountered.
Level 1
involves continuous supervision of train movement (i.e. the onboard computer is continuously supervising the maximum permitted speed and calculating the braking curve to the end of movement authority) while non-continuous communication occurs between train and trackside, generally through Eurobalises.
Lineside signals are necessary. Train detection and train integrity checks (i.e. the train is complete and has not been accidentally split) are performed by the trackside equipment beyond the scope of ERTMS.
Level 2
Involves continuous supervision of train movement with constant communication via GSM-R between the train and trackside.
Lineside signals are optional in this case, and train detection and train integrity checks are performed by the trackside equipment beyond the scope of ERTMS.
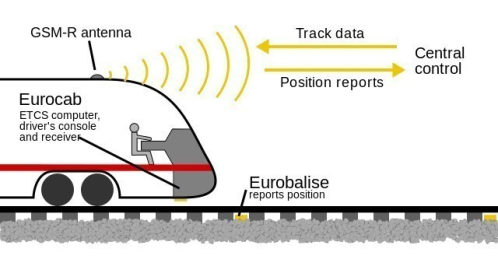
Level 3
Involves continuous train supervision with continuous communication between the train and trackside. The main difference with Level 2 is that train location and integrity are managed within the scope of the ERTMS system, i.e. there is no need for lineside signals or train detection systems on the trackside other than Eurobalises. Train integrity is supervised by the train.
In addition, there are two more levels: Level 0, which applies to trains equipped with ETCS running on non-equipped lines; and Level STM, which is meant for trains equipped with ETCS running on tracks where the Class B system needs to be operated. With regard to the STM level, ETCS acts as an interface between the driver and the national ATP.
ETCS LC
Low cost option for local routes. The system should work the same as L3, only the number of balises would be minimized. The balises would be used only in circuits with track branching, satellite navigation for locating the position of the train on the line is also considered.
What does ETCS consist of?
The ETCS equipment consists of a track-side and an on-board part. The information between them is in the form of data transmissions.
- Mobile or on-board part is mounted on vehicles
- Trackside or infrastructure part is installed along the tracks
Some variants of ETCS also use the GSM-R wireless network for communication between the track-side and mobile parts.
Operation modes in ETCS
| Abbreviation and DMI [de] symbol | Full name | Used
in level |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| FS | Full Supervision | 1, 2, 3 | The locomotive pulls the train, ETCS has all required information |
| LS
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/91/ERTMSmodeLS.svg/72px-ERTMSmodeLS.svg.png |
Limited Supervision | 1, 2, 3 | This mode is new to SRS 3.0.0 |
| OS
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e3/ERTMSmodeOS.svg/72px-ERTMSmodeOS.svg.png |
On Sight | 1, 2, 3 | On-sight ride |
| SR
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4d/ERTMSmodeSR.svg/72px-ERTMSmodeSR.svg.png |
Staff Responsible | 1, 2, 3 | The driver was granted permission to pass faulty signals |
| SH
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/01/ERTMSmodeSH.svg/72px-ERTMSmodeSH.svg.png |
Shunting | 0, 1, 2, 3 | |
| PS
(no symbol) |
Passive Shunting | 0, NTC, 1, 2, 3 | This mode is new to SRS 3.0.0 |
| UN
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7f/ERTMSmode_UN.svg/72px-ERTMSmode_UN.svg.png |
Unfitted | 0 | The line is not fitted with ETCS: the system will only observe master speed limit and train protection is left to older systems |
| SL
(no symbol) |
Sleeping | 0, NTC, 1, 2, 3 | Second locomotive controlled from the leading one |
| SB
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/02/ERTMSmodeSB.svg/72px-ERTMSmodeSB.svg.png |
Stand By | 0, NTC, 1, 2, 3 | |
| TR
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5b/ERTMSmodeTR.svg/72px-ERTMSmodeTR.svg.png |
Trip | NTC, 1, 2, 3 | |
| PT
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b7/ERTMSmodePT.svg/72px-ERTMSmodePT.svg.png |
Post Trip | 1, 2, 3 | The train overpassed the order to stop, full braking will be executed |
| SF
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d4/ERTMSmodeSF.svg/72px-ERTMSmodeSF.svg.png |
System Failure | 0, NTC, 1, 2, 3 | Trainborne ETCS equipment detected its failure |
| IS
(no symbol) |
Isolation | 0, NTC, 1, 2, 3 | Driver disconnected ETCS |
| NP
(no symbol) |
No Power | 0, NTC, 1, 2, 3 | |
| NL
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0c/ERTMSmodeNL.svg/72px-ERTMSmodeNL.svg.png |
Non Leading | 0, NTC, 1, 2, 3 | Second locomotive with its own driver |
| SE
(no symbol) |
STM European | NTC | This mode has not been implemented by any vendor and was removed by SRS 3.1.0 |
| SN
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/50/ERTMSmodeSN.svg/72px-ERTMSmodeSN.svg.png |
National System | NTC | |
| RV
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/30/ERTMSmodeRV.svg/72px-ERTMSmodeRV.svg.png |
Reversing | 1, 2, 3 |
ETCS test laboratories
Used materials:
https://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/European_Train_Control_System
https://www.spravazeleznic.cz/stavby-zakazky/modernizace/etcs/co-je-etcs
https://transport.ec.europa.eu/transport-modes/rail/ertms/how-does-it-work/etcs-levels-and-modes_en